集合的定义及实现
1. 什么是集合
集合通常是由一组无序的、不能重复的元素构成。
数学中常指的集合中的元素是可以重复的,但是计算机中集合的元素不能重复。
集合是特殊的数组。
- 特殊之处在于里面的元素没有顺序,也不能重复。
- 没有顺序意味着不能通过下标值进行访问,不能重复意味着相同的对象在集合中只会存在一份。
ES6 中的 Set 就是一个集合类,这里重新封装一个 Set 类,了解集合的底层实现:
2. 集合的实现
2.1 集合的属性和方法
add(value)向集合添加一个新的项。remove(value)从集合移除一个值。has(value)如果值在集合中,返回true,否则返回false。clear()移除集合中的所有项。size()返回集合所包含元素的数量。与数组的length属性类似。values()返回一个包含集合中所有值的数组。
// 集合结构的封装
class Set {
constructor() {
this.items = {};
}
// has(value) 判断集合中是否存在 value 值,存在返回 true,否则返回 false
has(value) {
return this.items.hasOwnProperty(value);
}
// add(value) 往集合中添加 value
add(value) {
if (this.has(value)) return false;
this.items[value] = value;
return true;
}
// remove(value) 删除集合中指定的 value
remove(value) {
// 如果集合不存在该 value,返回 false
if (!this.has(value)) return false;
delete this.items[value];
}
// clear() 清空集合中所有 value
clear() {
this.items = {};
}
// size() 获取集合中的 value 个数
size() {
return Object.keys(this.items).length;
}
// values() 获取集合中所有的 value
values() {
return Object.keys(this.items);
}
}
代码测试:
const set = new Set();
// add() 测试
set.add("abc");
set.add("abc");
set.add("123");
set.add("zxc");
console.log(set); //--> {items: {123: "123", abc: "abc", zxc: "zxc"}}
// has() 测试
console.log(set.has("123")); //--> true
console.log(set.has("456")); //--> false
// remove() 测试
set.remove("abc");
console.log(set); //--> {items: {123: "123", zxc: "zxc"}}
// size() 测试
console.log(set.size()); //--> 2
// values() 测试
console.log(set.values()); //--> ["123", "zxc"]
// clear() 测试
set.clear();
console.log(set.values()); //--> []
2.2 集合的操作
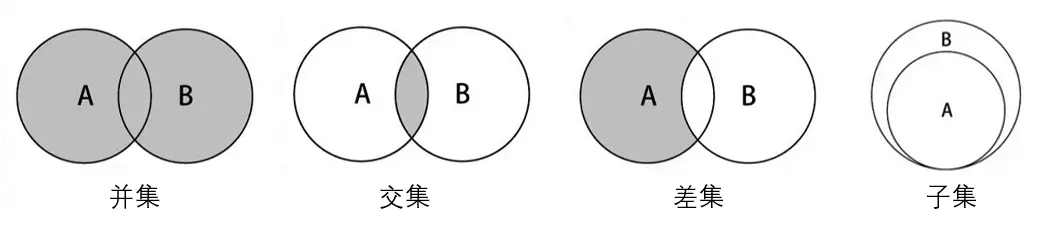
- 并集:对于给定的两个集合,返回一个包含两个集合中所有元素的新集合。
- 交集:对于给定的两个集合,返回一个包含两个集合中共有元素的新集合。
- 差集:对于给定的两个集合,返回一个包含所有存在于第一个集合且不存在于第二个集合的元素的新集合。
- 子集:验证一个给定集合是否是另一个集合的子集。
完整实现代码:
// 集合结构的封装
export default class Set {
constructor() {
this.items = {};
}
// has(value) 判断集合中是否存在 value 值,存在返回 true,否则返回 false
has(value) {
return this.items.hasOwnProperty(value);
}
// add(value) 往集合中添加 value
add(value) {
if (this.has(value)) return false;
this.items[value] = value;
return true;
}
// remove(value) 删除集合中指定的 value
remove(value) {
// 如果集合不存在该 value,返回 false
if (!this.has(value)) return false;
delete this.items[value];
}
// clear() 清空集合中所有 value
clear() {
this.items = {};
}
// size() 获取集合中的 value 个数
size() {
return Object.keys(this.items).length;
}
// values() 获取集合中所有的 value
values() {
return Object.keys(this.items);
}
// ------- 集合间的操作 ------- //
// union() 求两个集合的并集
union(otherSet) {
// 1、创建一个新集合
let unionSet = new Set();
// 2、将当前集合(this)的所有 value,添加到新集合(unionSet)中
for (let value of this.values()) {
unionSet.add(value);
}
// 3、将 otherSet 集合的所有 value,添加到新集合(unionSet)中
for (let value of otherSet.values()) {
unionSet.add(value); // add() 已经有重复判断
}
return unionSet;
}
// intersection() 求两个集合的交集
intersection(otherSet) {
// 1、创建一个新集合
let intersectionSet = new Set();
// 2、从当前集合中取出每一个 value,判断是否在 otherSet 集合中存在
for (let value of this.values()) {
if (otherSet.has(value)) {
intersectionSet.add(value);
}
}
return intersectionSet;
}
// difference() 差集
difference(otherSet) {
// 1、创建一个新集合
let differenceSet = new Set();
// 2、从当前集合中取出每一个 value,判断是否在 otherSet 集合中存在,不存在的即为差集
for (let value of this.values()) {
if (!otherSet.has(value)) {
differenceSet.add(value);
}
}
return differenceSet;
}
// subset() 子集
subset(otherSet) {
// 从当前集合中取出每一个 value,判断是否在 otherSet 集合中存在,有不存在的返回 false
// 遍历完所有的,返回 true
for (let value of this.values()) {
if (!otherSet.has(value)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}