JS 编译流程与 AST 语法树
要了解 JS 编译执行的原理,就得先了解 AST,目前前端常用的一些插件或者工具,例如编辑器的错误提示、代码格式化(ESLint、Prettier)、代码高亮、代码自动补全、代码压缩、Babel、CSS 预处理器等,都建立在 AST 的基础之上。
一、JS 编译执行流程
JS 执行的第一步是读取 JS 文件中的字符流,然后通过词法分析生成 Token,之后再通过语法分析(Parser)生成 AST(Abstract Syntax Tree),最后生成机器码执行。
整个解析过程分为以下两个步骤:
- 词法分析:将代码分割成最小语法单元数组
- 语法分析:在词法分析的基础上建立分析语法单元间的关系
JS Parser 是 JS 语法解析器,它可以将 JS 源码转成 AST,常见的 Parser 有 esprima、traceur、acorn、shift 等。
点击查看 Parser API 规范
二、词法分析和语法分析
1、词法分析
词法分析,也称之为扫描(scanner),就是调用 next() 方法,将字符串形式的代码转换为一个语法片段 Tokens 数组,同时过滤掉源程序中的注释和空白符(换行符、空格、制表符)等。
- Token(令牌):一个不可分割的最小单元,例如
var这三个字符,只能作为一个整体,语义上不能再被分解,是一个 Token。另外,每个标识符是一个 Token,每个操作符是一个 Token,每个标点符号也是一个 Token; Tokens(令牌流):一个由 Token 组成的数组,内部可以是数字、标签、标点符号、运算符等。
// 示例源码
a + b
// Tokens
[
{ type: { ... }, value: "a", start: 0, end: 1, loc: { ... } },
{ type: { ... }, value: "+", start: 2, end: 3, loc: { ... } },
{ type: { ... }, value: "b", start: 4, end: 5, loc: { ... } },
]
2、语法分析
语法分析阶段会把 Tokens 转换成抽象语法树 AST,同时验证语法,抛出语法错误。
三、什么是 AST 抽象语法树
AST(Abstract Syntax Tree)抽象语法树,是源代码语法结构的一种抽象表示,以树状的形式表现编程语言的语法结构,树上的每个节点都表示源代码中的一种结构。
举个例子:
- 源代码1
- 源代码2
function add(a, b) {
return a + b
}
function getA() {
const a = 123
return a
}
- 源代码1 的 AST 结构
- 源代码2 的 AST 结构
FunctionDeclaration {
id: Identifier {
name:"add"
},
params: {
Identifier {
name:"a"
},
Identifier {
name:"b"
},
},
body: BlockStatement {
body: {
ReturnStatement {
argument: BinaryExpression {
left: Identifier {
name:"a"
},
operator:"+",
right: Identifier {
name:"b"
},
}
}
}
}
}
FunctionDeclaration {
id: Identifier { ... },
body: BlockStatement {
body: {
VariableDeclaration {
declarations: {
VariableDeclaration {
id: Identifier {
name: "a"
},
init: initNumericLiteral {
extra: {
rawValue:123,
raw:"123"
},
value:123
}
}
},
kind:"const"
},
ReturnStatement {
argument: Identifier {
name: "a"
}
}
}
}
}
JS 代码可以直接通过 AST explorer 或 VSCode 的 babel-ast-explorer 插件查看其 AST 结构。
四、AST 语法树的应用
1、@babel/parser 转 AST
@babel/parser 基于 acorn 和 acorn-jsx,是 Babel 中的 JS 解析器,用于将 JS 代码转为 AST,安装如下:
yarn add @babel/parser --dev
使用:
import { parse } from '@babel/parser'
function compile(code) {
const ast = parse(code)
console.log(ast)
}
const code = `
function add(a, b) {
return a + b
}
`
compile(code)
输出:
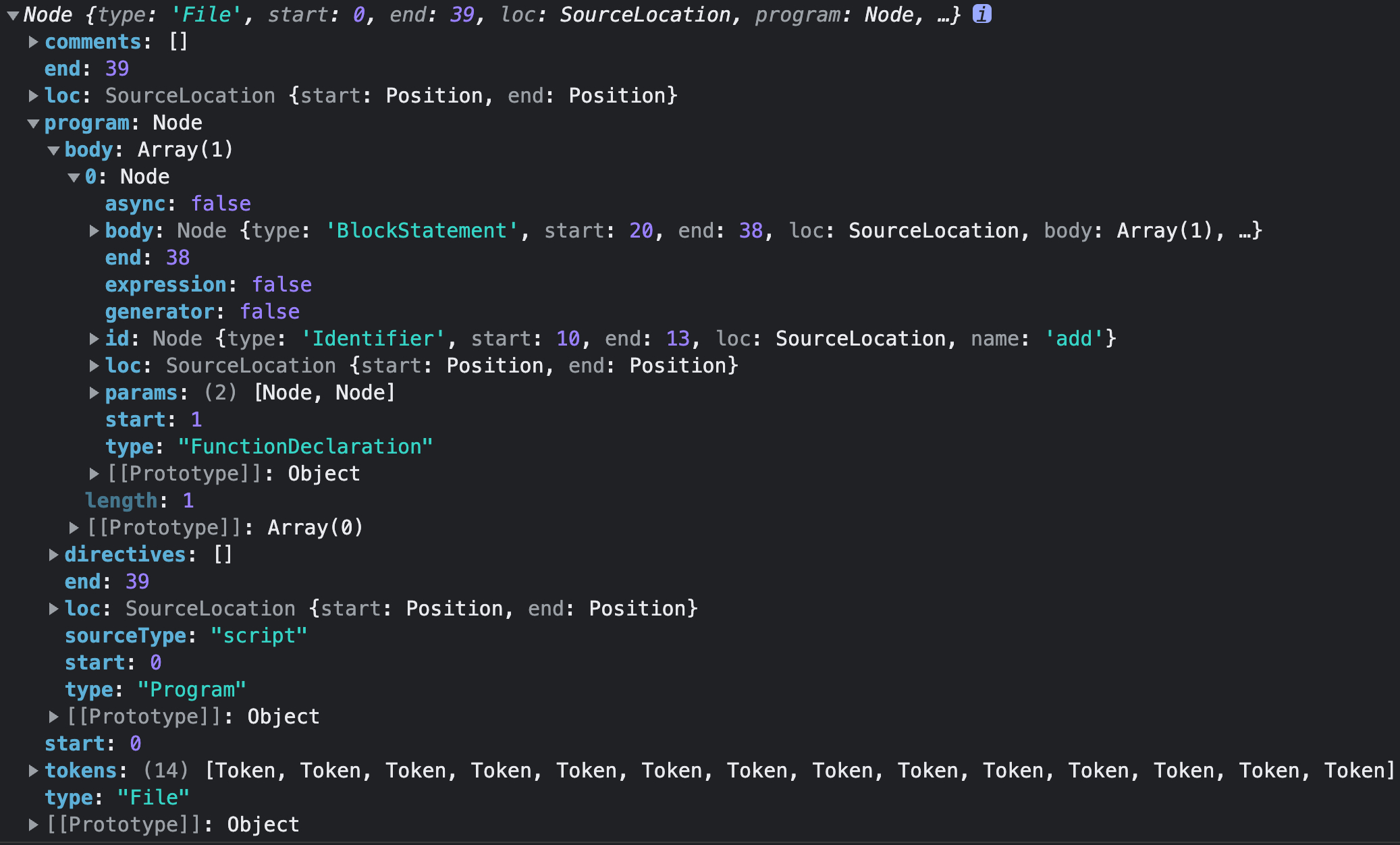
2、@babel/generator 转回 JS
@babel/generator 用于将 AST 结构转回 JS 代码,安装如下:
yarn add @babel/generator --dev
使用:
import { parse } from '@babel/parser'
import generate from '@babel/generator'
function compile(code) {
const ast = parse(code)
const output = generate(ast)
console.log(output)
}
const code = `
function add(a, b) {
return a + b
}
`
compile(code)
输出:
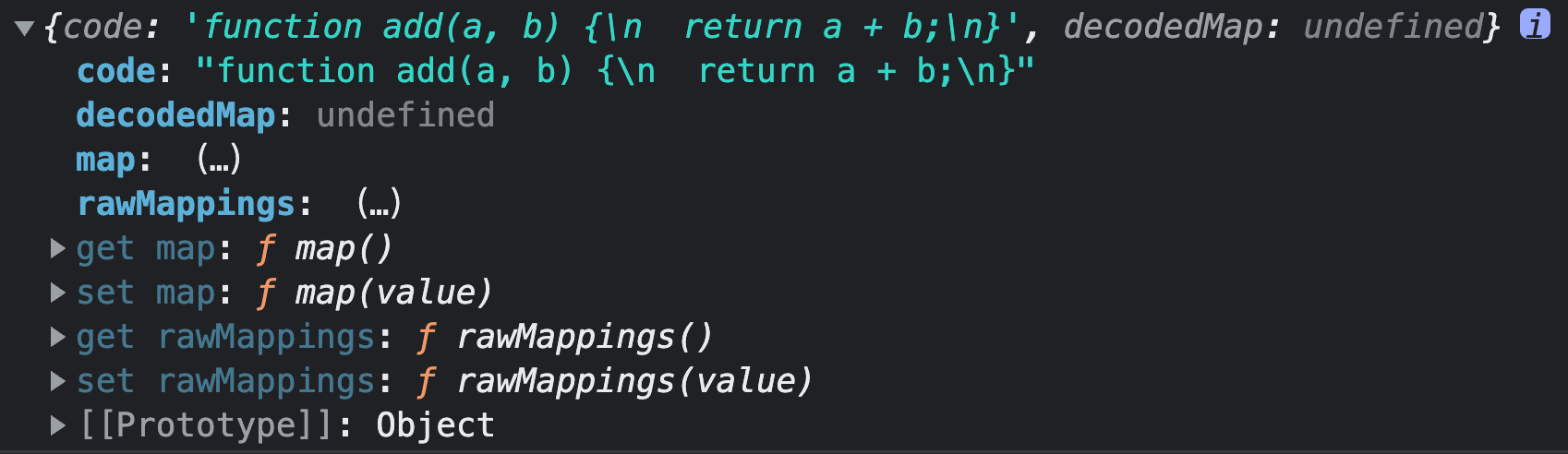
运行如果出现 process is not defined、Buffer is not defined 等问题,可通过在项目 config 文件中进行配置来解决。
webpack 解决方法:
yarn add process buffer
webpack.config.js:
const webpack = require('webpack')
module.exports = {
// ...
plugins: [
// ...
new webpack.ProvidePlugin({
process: 'process/browser',
}),
new webpack.ProvidePlugin({
Buffer: ['buffer', 'Buffer'],
}),
]
}
3、中间处理 AST 结构的过程
对代码的处理就是在 JS 转成 AST 后,对 AST 节点进行递归遍历并修改,最后将修改后的 AST 转回 JS 代码。
3-1、@babel/traverse 遍历 AST
@babel/traverse 用于对 AST 节点进行递归遍历,安装如下:
yarn add @babel/traverse --dev
通过 traverse 打印出每个节点:
import { parse } from '@babel/parser'
import generate from '@babel/generator'
import traverse from "@babel/traverse"
function compile(code) {
const ast = parse(code)
traverse(ast, {
enter(path) {
// 打印出每个节点
console.log(path)
},
});
const output = generate(ast)
return output
}
const code = `
function add(a, b) {
return a + b
}
`
compile(code)
输出:
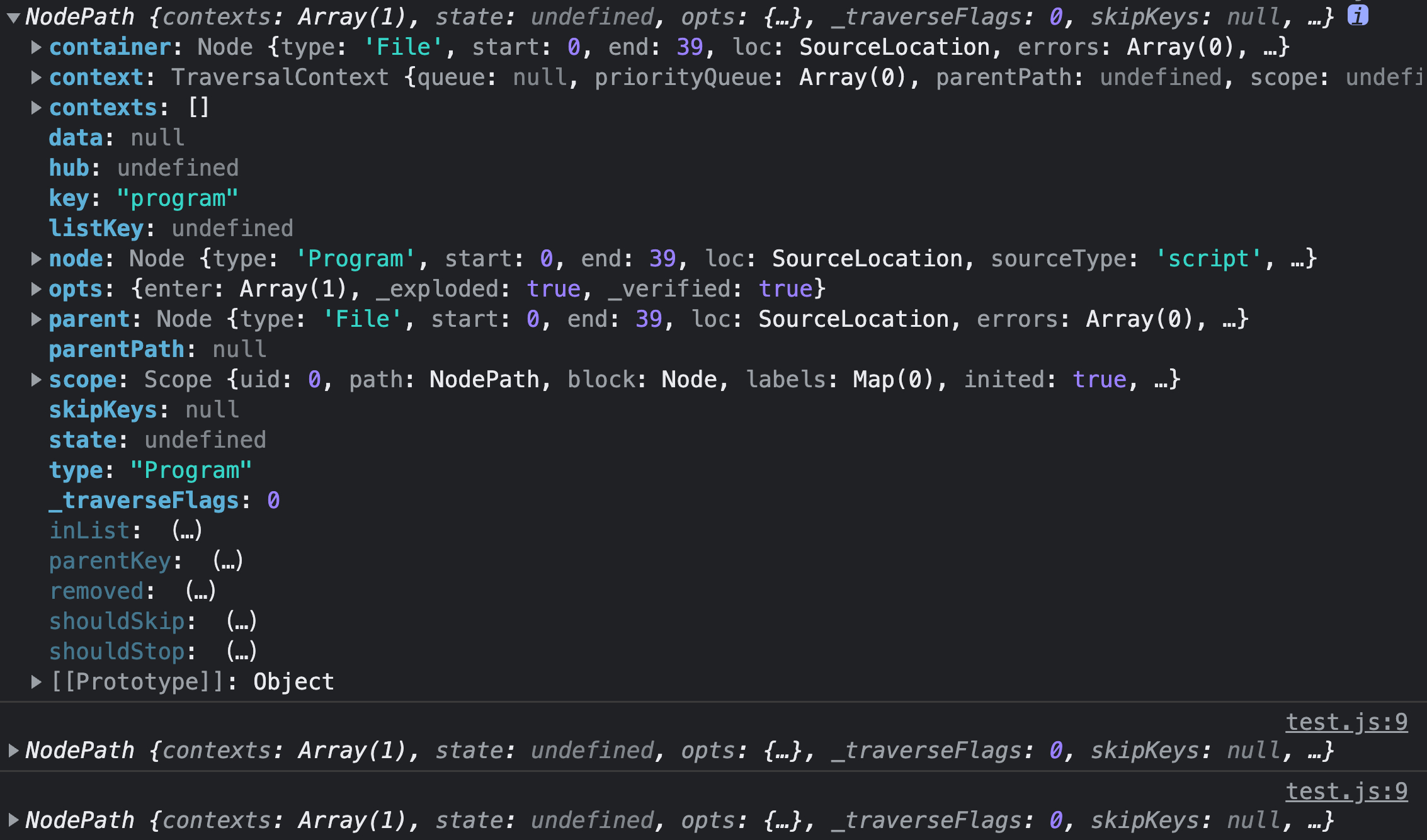
traverse 遍历过程中可以对节点进行修改,例如通过 traverse 将 a + b 替换成 a * b:
import { parse } from '@babel/parser'
import generate from '@babel/generator'
import traverse from "@babel/traverse"
function compile(code) {
const ast = parse(code)
traverse(ast, {
enter(path) {
if (path.isBinaryExpression({ operator: "+" })) {
path.node.operator = "*";
}
},
});
const output = generate(ast)
return output
}
const code = `
function add(a, b) {
return a + b
}
`
const newCode = compile(code)
console.log(newCode)
输出:

3-2、@babel/types 修改 AST
上面通过 traverse 对 AST 进行遍历并修改,而 @babel/types 是一个用于处理 AST 节点的 Lodash 式工具库,提供了构造、验证以及变换 AST 节点的方法,可更方便的对 AST 节点进行修改,安装如下:
yarn add @babel/types --dev
使用:
import { parse } from '@babel/parser'
import generate from '@babel/generator'
import traverse from "@babel/traverse"
import * as t from "@babel/types"
function compile(code) {
const ast = parse(code)
traverse(ast, {
enter(path) {
if (path.isBinaryExpression({ operator: "+" })) {
if (t.isBinaryExpression(path.node, { operator: "+" })) {
path.node.operator = "*";
}
},
});
const output = generate(ast)
return output
}
const code = `
function add(a, b) {
return a + b
}
`
const newCode = compile(code)
console.log(newCode)
4、应用实例
举个例子,通过 AST “手术刀”,给每次调用 console.log(xx) 时在前面打印函数名,方便 log 打印调试时知道是哪个函数调用的:
import { parse } from '@babel/parser'
import generate from '@babel/generator'
import traverse from "@babel/traverse"
import * as t from "@babel/types"
const visitor = {
enter(path) {
const { callee } = path.node
const isConsoleLog =
t.isMemberExpression(callee) &&
callee.object.name === "console" &&
callee.property.name === "log"
if (isConsoleLog) {
const funcPath = path.findParent(p => {
return p.isFunctionDeclaration()
})
const funcName = funcPath.node.id.name
path.node.arguments.unshift(t.stringLiteral(funcName))
}
}
}
function compile(code) {
const ast = parse(code)
traverse(ast, visitor)
const output = generate(ast, {}, code)
return output
}
const code = `
function getData() {
console.log('data')
}
`
const newCode = compile(code)
console.log(newCode.code)
输出:
五、AST 节点说明汇总
1、Identifier
标识符,即写 JS 时自定义的名称,如变量名,函数名,属性名等。相应的接口如下:
interface Identifier <: Expression, Pattern {
type: "Identifier";
name: string;
}
2、Literal
字面量,这里不是指 [] 或 {},而是本身语义就代表一个值的字面量,如 1,“hello”, true 这些,以及正则表达式如 /\d?/:
interface Literal <: Expression {
type: "Literal";
value: string | boolean | null | number | RegExp; // 对应字面量的值
}
3、RegExpLiteral
针对正则字面量,用于解析正则表达式的内容,添加多一个 regex 字段,里面包括正则本身以及正则的 flags。
interface RegExpLiteral <: Literal {
regex: {
pattern: string;
flags: string;
};
}
4、Programs
一般作为根节点,代表一棵完整的程序代码树。
interface Program <: Node {
type: "Program";
body: [ Statement ]; // 一个数组,包含多个 Statement(即语句)节点
}
5、Functions
函数声明或函数表达式节点。
interface Function <: Node {
id: Identifier | null; // 函数名
params: [ Pattern ]; // 是一个表示参数的数组
body: BlockStatement; // 块语句
}
测试过程中不会找到 type: "Function" 节点,但可以找到 type: "FunctionDeclaration" 和 type: "FunctionExpression",因为函数要么以声明语句出现,要么以函数表达式出现,都是节点类型的组合类型。
6、Statement
一个语句节点,是一种区分。
interface Statement <: Node { }
7、ExpressionStatement
表达式语句节点,a = a + 1 或 a++ 中会有一个 expression 属性指向一个表达式节点对象。
interface ExpressionStatement <: Statement {
type: "ExpressionStatement";
expression: Expression;
}
8、BlockStatement
块语句节点。举个例子:
if (...) { // 这里是块语句的内容 } 块中可包含多个其他语句,所以有一个 body 属性,是一个数组,表示了块里面的多个语句。
interface BlockStatement <: Statement {
type: "BlockStatement";
body: [ Statement ];
}
9、EmptyStatement
一个空语句节点,没有执行任何有用的代码,例如一个单独的分号 ;
interface EmptyStatement <: Statement {
type: "EmptyStatement";
}
10、DebuggerStatement
即 debugger。
interface DebuggerStatement <: Statement {
type: "DebuggerStatement";
}
11、WithStatement
with 语句节点。
interface WithStatement <: Statement {
type: "WithStatement";
object: Expression; // 表示 with 要使用的对象
body: Statement; // 对应 with 后边要执行的语句
}
12、控制流语句
12-1、ReturnStatement
返回语句节点。
interface ReturnStatement <: Statement {
type: "ReturnStatement";
argument: Expression | null; // 代表返回的内容
}
12-2、LabeledStatement
label 语句,举个例子:
loop: for(let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// ...
for (let j = 0; j < min; j++) {
// ...
break loop;
}
}
这里的 loop 就是一个 label,可以在循环嵌套中使用 break loop 来指定跳出哪个循环。label 语句指的就是 loop: ...。
interface LabeledStatement <: Statement {
type: "LabeledStatement";
label: Identifier; // label 的名称
body: Statement; // 指向对应的语句,通常是循环或 switch 语句
}
12-3、BreakStatement
break 语句节点。
interface BreakStatement <: Statement {
type: "BreakStatement";
label: Identifier | null; // 表示需要的 label 名称,当不需要 label 时为 null
}
12-4、ContinueStatement
continue 语句节点,和 break 类似。
interface ContinueStatement <: Statement {
type: "ContinueStatement";
label: Identifier | null;
}
13、条件语句
13-1、IfStatement
if 语句节点。
interface IfStatement <: Statement {
type: "IfStatement";
test: Expression; // 表示 if (...) 括号中的表达式
consequent: Statement; // 表示条件为 true 时的执行语句,通常是块语句
// alternate 表示 else 后跟随的语句节点,通常是块语句
// 也可以是个 if 语句节点,即 if (a) { //... } else if (b) { // ... }
// 也可以为 null
alternate: Statement | null;
}
13-2、SwitchStatement
switch 语句节点。
interface SwitchStatement <: Statement {
type: "SwitchStatement";
discriminant: Expression; // 表示 switch 语句后紧随的表达式,通常会是一个变量
cases: [ SwitchCase ]; // 一个 case 节点的数组,用来表示各个 case 语句
}
13-3、SwitchCase
switch 的 case 节点。
interface SwitchCase <: Node {
type: "SwitchCase";
test: Expression | null; // 表示 case 的判断表达式,为 null 时表示 default 这个 case 节点
consequent: [ Statement ]; // 表示 case 的执行语句
}
14、异常语句
14-1、ThrowStatement
throw 语句节点。
interface ThrowStatement <: Statement {
type: "ThrowStatement";
argument: Expression; // 表示 throw 后边紧跟的表达式
}
14-2、TryStatement
try 语句节点。
interface TryStatement <: Statement {
type: "TryStatement";
block: BlockStatement; // 表示 try 的执行语句,通常是一个块语句
handler: CatchClause | null; // 指 catch 节点
// finalizer 指 finally 语句节点,为 null 时必须是个块语句节点
finalizer: BlockStatement | null;
}
14-3、CatchClause
catch 节点。
interface CatchClause <: Node {
type: "CatchClause";
param: Pattern; // 表示 catch 后的参数
body: BlockStatement; // 表示 catch 后的执行语句,通常是个块语句
}
15、循环语句
15-1、WhileStatement
while 语句节点。
interface WhileStatement <: Statement {
type: "WhileStatement";
test: Expression; // 表示括号中的表达式
body: Statement; // 表示要循环执行的语句
}
15-2、DoWhileStatement
do/while 语句节点,和 while 语句类似。
interface DoWhileStatement <: Statement {
type: "DoWhileStatement";
body: Statement;
test: Expression;
}
15-3、ForStatement
for 循环语句节点。
init/test/update 三个属性都可以为 null,即 for(;;){}。
interface ForStatement <: Statement {
type: "ForStatement";
init: VariableDeclaration | Expression | null; // 初始化值
test: Expression | null; // 循环判断条件
update: Expression | null; // 每次循环执行的变量更新语句
body: Statement; // 表示要循环执行的语句
}
15-4、ForInStatement
for/in 语句节点。
interface ForInStatement <: Statement {
type: "ForInStatement";
left: VariableDeclaration | Pattern; // in 关键词左侧语句
right: Expression; // in 关键词右侧语句
body: Statement; // 表示要循环执行的语句
}
16、声明语句
16-1、Declarations
声明语句节点,同样也是语句,只是一个类型的细化。
interface Declaration <: Statement { }
16-2、FunctionDeclaration
函数声明,和之前 Function 不同的是,id 不能为 null。
interface FunctionDeclaration <: Function, Declaration {
type: "FunctionDeclaration";
id: Identifier;
}
16-3、VariableDeclaration
变量声明。
interface VariableDeclaration <: Declaration {
type: "VariableDeclaration";
declarations: [ VariableDeclarator ]; // 表示声明的多个描述,例如:let a = 1, b = 2;
kind: "var"; // 表示是什么类型的声明,因为 ES6 引入了 const/let
}
16-4、VariableDeclarator
变量声明的描述。
interface VariableDeclarator <: Node {
type: "VariableDeclarator";
id: Pattern; // 表示变量名称节点
init: Expression | null; // 表示初始值的表达式,可以为 null
}
17、表达式语句
17-1、Expressions
表达式节点。
interface Expression <: Node { }
17-2、ThisExpression
表示 this。
interface ThisExpression <: Expression {
type: "ThisExpression";
}
17-3、ArrayExpression
数组表达式节点。
interface ArrayExpression <: Expression {
type: "ArrayExpression";
elements: [ Expression | null ]; // 一个数组,表示数组的多个元素,每一个元素都是一个表达式节点
}
17-4、ObjectExpression
对象表达式节点。
interface ObjectExpression <: Expression {
type: "ObjectExpression";
properties: [ Property ]; // 一个数组,表示对象的每一个键值对,每个元素都是一个属性节点
}
17-5、Property
对象表达式中的属性节点。
interface Property <: Node {
type: "Property";
key: Literal | Identifier; // 表示键
value: Expression; // 表示值
// 由于 ES5 语法中有 get/set 的存在,所以有 kind 来表示普通的初始化,或 get/set
kind: "init" | "get" | "set";
}
17-6、FunctionExpression
函数表达式节点。
interface FunctionExpression <: Function, Expression {
type: "FunctionExpression";
}
18、一元运算符表达式
18-1、UnaryExpression
一元运算表达式节点(++/-- 是 update 运算符,不在这个范畴内)
interface UnaryExpression <: Expression {
type: "UnaryExpression";
operator: UnaryOperator; // 表示运算符
prefix: boolean; // 表示是否为前缀运算符
argument: Expression; // 要执行运算的表达式
}
18-2、UnaryOperator
一元运算符,枚举类型,所有值如下:
enum UnaryOperator {
"-" | "+" | "!" | "~" | "typeof" | "void" | "delete"
}
18-3、UpdateExpression
update 运算表达式节点,即 ++/--,和一元运算符类似,只是 operator 指向的节点对象类型不同,这里是 update 运算符。
interface UpdateExpression <: Expression {
type: "UpdateExpression";
operator: UpdateOperator;
argument: Expression;
prefix: boolean;
}
18-4、UpdateOperator
update 运算符,值为 ++ 或 --,配合 update 表达式节点的 prefix 属性来表示前后。
enum UpdateOperator {
"++" | "--"
}
19、二元运算符表达式
19-1、BinaryExpression
二元运算表达式节点。
interface BinaryExpression <: Expression {
type: "BinaryExpression";
operator: BinaryOperator; // 二元运算符
left: Expression; // 运算符左侧表达式
right: Expression; // 运算符右侧表达式
}
BinaryOperator 二元运算符,所有值如下:
enum BinaryOperator {
"==" | "!=" | "===" | "!=="
| "<" | "<=" | ">" | ">="
| "<<" | ">>" | ">>>"
| "+" | "-" | "*" | "/" | "%"
| "|" | "^" | "&" | "in"
| "instanceof"
}
19-2、AssignmentExpression
赋值表达式节点。
interface AssignmentExpression <: Expression {
type: "AssignmentExpression";
operator: AssignmentOperator; // 赋值运算符
left: Pattern | Expression; // 赋值运算符左侧表达式
right: Expression; // 赋值运算符右侧表达式
}
AssignmentOperator 赋值运算符,所有值如下:
enum AssignmentOperator {
"=" | "+=" | "-=" | "*=" | "/=" | "%="
| "<<=" | ">>=" | ">>>="
| "|=" | "^=" | "&="
}
19-3、LogicalExpression
逻辑运算表达式节点,和赋值或者二元运算类型,只不过 operator 是逻辑运算符类型。
interface LogicalExpression <: Expression {
type: "LogicalExpression";
operator: LogicalOperator;
left: Expression;
right: Expression;
}
LogicalOperator 逻辑运算符,两种值,即与或。
enum LogicalOperator {
"||" | "&&"
}
19-4、MemberExpression
成员表达式节点。
interface MemberExpression <: Expression, Pattern {
type: "MemberExpression";
object: Expression; // 引用对象的表达式节点
property: Expression; // 表示属性名称
// computed 为 false 表示 . 来引用成员,是一个 Identifier 节点
// computed 为 true 表示 [] 来进行引用,是一个 Expression 节点,名称是表达式的结果值
computed: boolean;
}
20、其他表达式
20-1、ConditionalExpression
条件表达式,通常称为三元运算表达式,即 boolean ? true : false。属性参考条件语句。
interface ConditionalExpression <: Expression {
type: "ConditionalExpression";
test: Expression;
alternate: Expression;
consequent: Expression;
}
20-2、CallExpression
函数调用表达式。
interface CallExpression <: Expression {
type: "CallExpression";
callee: Expression; // 一个表达式节点,表示函数
arguments: [ Expression ]; // 是一个数组,元素是表达式节点,表示函数参数列表
}
20-3、NewExpression
new 表达式。
interface NewExpression <: CallExpression {
type: "NewExpression";
}
20-4、SequenceExpression
逗号运算符构建的表达式。
interface SequenceExpression <: Expression {
type: "SequenceExpression";
expressions: [ Expression ]; // 一个数组,即表示构成整个表达式,被逗号分割的多个表达式
}
20-5、Patterns
模式,主要在 ES6 的解构赋值中有意义,在 ES5 中,可以理解为和 Identifier 差不多的东西。
interface Pattern <: Node { }
AST 节点详情具体可查看 ESTree