Express〡Koa 中间件机制
一、中间件的定义
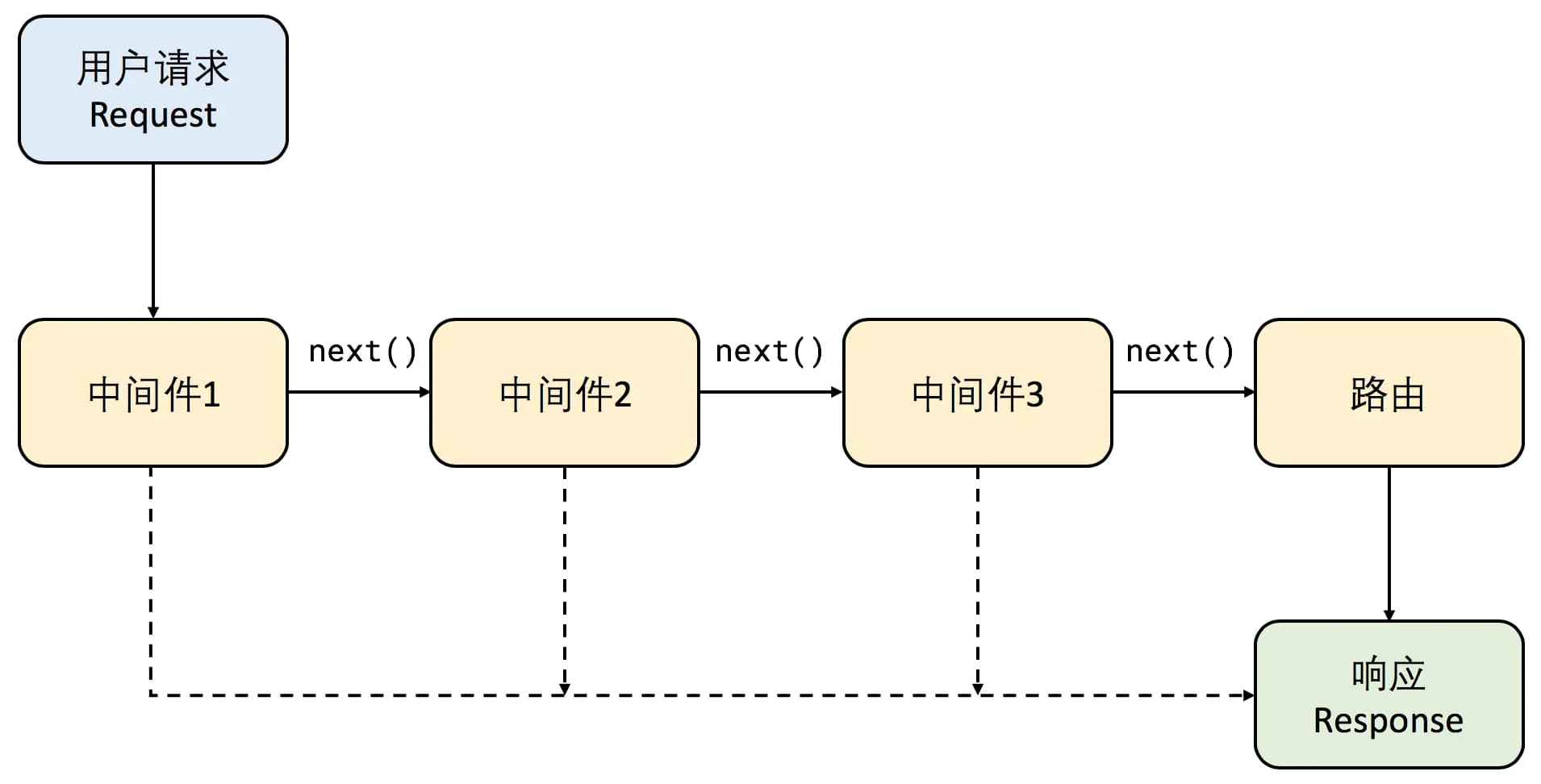
中间件(middleware)即处理 HTTP 请求的函数,在匹配请求路由时进行一系列的操作,如果中间件中调用了 next() 方法,则会继续往下匹配。
二、中间件的使用
1、Express 中间件的使用
Express 的中间件是一个函数,接收的三个参数分别为:
request对象(代表 HTTP 请求)response对象(代表 HTTP 回应)next回调函数(用来触发下一个中间件的执行)
function someMiddleware(req, res, next) {
// 自定义逻辑
// ...
next();
}
注意,如果中间件既没调用 next 函数,又不返回响应时,服务器会直接卡在这个中间件不会继续执行下去。
中间件的使用示例:
通过 app.use 等函数可以注册中间件,默认对所有路径生效,可通过第一个参数在指定路径下执行(如果参数是 * 也代表对所有路径有效),举个例子:
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
// 注册第一个中间件(在所有路径下执行)
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('在任何请求时执行', req.method, req.url)
next()
})
// 注册第二个中间件(在 /api、/api/a 等路径下执行)
app.use('/api', (req, res, next) => {
console.log('处理 /api... 路由')
next()
})
// 注册第三个中间件(在 get 请求且指定路径下执行)
app.get('/api', (req, res, next) => {
console.log('get /api... 路由')
next()
})
// 注册第四个中间件(在 post 请求且指定路径下执行)
app.post('/api', (req, res, next) => {
console.log('post /api... 路由')
next()
})
// 注册第五个中间件(在所有路径下执行)
app.use('*', (req, res, next) => {
console.log('处理 404')
res.json({
errno: -1,
msg: '404 not fount'
})
})
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('server is running on port 3000')
})
上面代码注册了五个中间件。收到 HTTP 请求后,依次执行:
- 调用第一个中间件,在控制台输出信息,然后通过 next 方法,执行下一个中间件;
- 如果请求的是
/api理由,将依次进入第二/三/四个中间件,否则直接进入第五个中间件; - 第五个中间件没有调用
next方法,返回响应,不再向后传递。
2、Koa 中间件的使用
与 Express 一样,通过 app.use 等函数注册中间件:
const Koa = require('koa')
const app = new Koa()
// 注册第一个中间件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
console.log('1、第一个中间件1')
await next()
console.log('2、第一个中间件2')
})
// 注册第二个中间件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
console.log('3、第二个中间件1')
await next()
console.log('4、第二个中间件2')
})
// 注册第三个中间件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
console.log('5、第三个中间件1')
await next()
console.log('6、第三个中间件2')
})
app.listen(3333, () => {
console.log('server is running on port 3333')
})
运行结果:
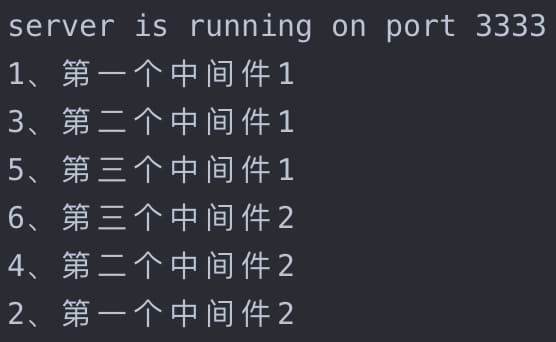
可以看到,Koa 的中间件是洋葱圈模型,执行顺序与 Express 不同。
三、中间件的原理
1、Express 中间件原理
Express 中间件的原理是维护一个类似管道的中间件任务队列,根据先进先出的顺序依次处理每个中间件。
2、Koa 中间件原理
koa 使用洋葱圈模型的函数调用栈执行中间件:
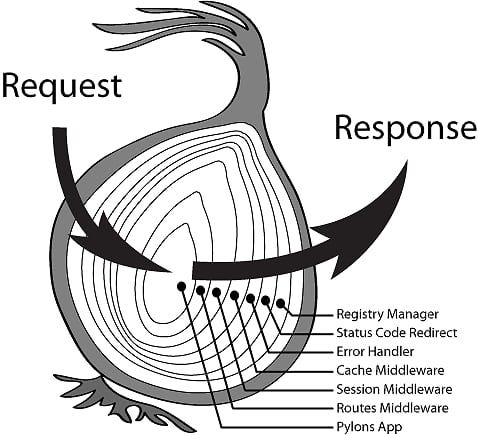
原理是在中间件之间通过 next 函数联系,当一个中间件调用 next() 后,会将控制权交给下一个中间件,直到下一个中间件不再执行 next() 时沿路返回,依次将控制权交给上一个中间件。
四、编写中间件
1、编写 Express 中间件
- 新建登录验证中间件
- 使用登录验证中间件
const { ErrorModel } = require('../model/resModel');
module.exports = (req, res, next) => {
if (req.session.username) {
next()
} else {
res.json(new ErrorModel('尚未登录'))
}
}
// ...
const loginCheckMiddleware = require('../middleware/loginCheck')
// 新建博客
router.post('/new', loginCheckMiddleware, (req, res, next) => {
const result = newBlog(req.body, req.session.username)
return result.then(data => {
res.json(new SuccessModel(data))
})
});
2、编写 Koa 中间件
- 新建登录验证中间件
- 使用登录验证中间件
const { ErrorModel } = require('../model/resModel');
module.exports = async (ctx, next) => {
if (ctx.session.username) {
await next()
} else {
ctx.body = new ErrorModel('尚未登录')
}
}
// ...
const loginCheckMiddleware = require('../middleware/loginCheck')
// 新建博客
router.post('/new', loginCheckMiddleware, async (ctx, next) => {
const result = await newBlog(ctx.request.body, ctx.session.username)
ctx.body = new SuccessModel(result)
});
五、模拟实现一个 Express
下面来模拟实现一个 Express:
- 实现中间件函数的注册;
- 实现中间件函数中核心的
next机制; - 路由处理,对路径进行匹配。
1、Express 类的基本结构
确定类要实现的主要方法:
use():实现通用的中间件注册;get()、post():实现与 http 请求相关的中间件注册;listen():相当于 httpServer 的listen()函数,可直接在类的listen()函数中创建 httpServer,透传 server 参数,监听请求,并执行回调函数(req, res) => {}。
LikeExpress 类基本结构如下:
const http = require('http');
class LikeExpress {
constructor() { }
use() { }
get() { }
post() { }
// httpServer 回调函数
callback() {
return (req, res) => {
res.json = (data) => {
res.setHeader('Content-type', 'application/json');
res.end(JSON.stringify(data));
};
}
}
listen(...args) {
const server = http.createServer(this.callback());
// 参数透传到 httpServer 中
server.listen(...args);
}
}
module.exports = () => {
return new LikeExpress();
}
2、中间件注册
从 app.use([path,] callback [, callback...]) 可以看出,中间件可以是函数数组,也可以是单个函数,为了简化实现,统一将中间件处理为函数数组。而 LikeExpress 类可以实现中间件注册的方法有:use()、get()、post(),因此考虑:
- 抽象出通用的中间件注册函数;
- 为这三个方法建立 3 个中间件函数数组,存放不同请求的中间件。
use()是所有请求通用的中间件注册方法,因此存放use()中间件的数组是get()和post()的并集。
2-1、中间件队列数组
中间件数组需要存放在公用的地方,以便类中的方法都能读取到中间件,所以将中间件数组放在 constructor() 构造函数中:
constructor() {
// 存放中间件的列表
this.routes = {
all: [], // 通用的中间件
get: [], // get 请求的中间件
post: [], // post 请求的中间件
};
}
2-2、中间件注册函数
中间件注册,即把中间件存入对应的中间件数组中。
中间件注册函数需要解析传入的参数,第一个参数可能是路由,也可能是中间件,所以需要判断第一个参数是否为路由,如果是路由,则将路由原样输出;否则默认是根路由。再将剩余中间件参数转换为数组。
register(path) {
const info = {};
// 如果第一个参数是路由
if (typeof path === "string") {
info.path = path;
// 从第二个参数开始,转为数组,存入中间件数组 stack 中
info.stack = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1);
} else {
// 如果第一个参数不是路由,则默认是根路由,全部路由都会执行
info.path = '/';
// 从第一个参数开始,转换为数组,存入中间件数组 stack 中
info.stack = slice.call(arguments, 0);
}
return info;
}
2-3、实现 use()、get()、post()
有了通用的中间件注册函数 register(),就可以基于 register() 实现 use()、get()、post(),将中间件存入相应的中间件数组中:
use() {
const info = this.register.apply(this, arguments);
this.routes.all.push(info);
}
get() {
const info = this.register.apply(this, arguments);
this.routes.get.push(info);
}
post() {
const info = this.register.apply(this, arguments);
this.routes.post.push(info);
}
3、路由匹配处理
当注册函数中第一个参数为路由时,只有当请求路径与路由匹配或是它的子路由时,才会触发相应的中间件函数。所以需要一个路由匹配函数,根据请求方法和请求路径,取出匹配路由的中间件数组,供后续的 callback() 去执行:
match(method, url) {
let stack = [];
// 忽略浏览器自带的 icon 请求
if (url === "/favicon.ico") {
return stack;
}
// 获取 routes
let curRoutes = [];
curRoutes = curRoutes.concat(this.routes.all); // use() 会在所有路由执行
curRoutes = curRoutes.concat(this.routes[method]); // 根据请求方法获取对应路由
curRoutes.forEach(route => {
if (url.indexOf(route.path) === 0) {
// 判断是否属于当前路由或子路由,如果是,则取出
stack = stack.concat(route.stack);
}
})
return stack;
}
然后在 httpServer 的回调函数 callback() 中取出需要执行的中间件:
callback() {
return (req, res) => {
res.json = (data) => {
res.setHeader('Content-type', 'application/json');
res.end(JSON.stringify(data));
};
// 根据请求方法和路径,区分哪些中间件函数需要执行
const url = req.url;
const method = req.method.toLowerCase();
const resultList = this.match(method, url);
// handle 是核心的 next 机制
this.handle(req, res, resultList);
}
}
4、next 机制实现
express 的中间件函数参数是:req, res, next,next 参数是一个函数,只有调用它才可以使中间件函数一个一个按顺序执行下去,与 ES6 Generator 中的 next() 类似,实现一个 next()函数需要:
- 从中间件队列数组里每次按次序取出一个中间件;
- 把
next()函数传入到取出的中间件中。由于中间件数组是公用的,每次执行next()都会从中间件数组中取出第一个中间件函数执行,从而实现了中间件按次序的效果。
// 核心的 next 机制
handle(req, res, stack) {
const next = () => {
// 中间件队列出队,拿到第一个匹配的中间件
// stack 数组是同一个,所以每执行一次 next(),都会取出下一个中间件
const middleware = stack.shift();
if (middleware) {
// 执行中间件函数
middleware(req, res, next);
}
}
// 立马执行
next();
}
5、测试实现的 Express
下面验证 LikeExpress 类是否实现了中间件注册、路由匹配以及 next 机制:
- test.js
- like-express.js
const express = require('./like-express');
const app = express();
// 注册第一个中间件
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('请求开始...', req.method, req.url);
next();
})
// 注册第二个中间件
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('处理 cookie...');
req.cookie = {
useId: "test"
};
next();
})
// 注册第三个中间件
app.use('/api', (req, res, next) => {
console.log('处理 /api 路由');
next();
})
// 注册第四个中间件
app.get('/api', (req, res, next) => {
console.log('get /api 路由');
next();
})
app.listen(7878, () => {
console.log('server is running at 7878');
})
const http = require('http');
const slice = Array.prototype.slice;
class LikeExpress {
constructor() {
// 存放中间件的列表
this.routes = {
all: [],
get: [],
post: [],
};
}
register(path) {
const info = {};
// 如果第一个参数是路由
if (typeof path === "string") {
info.path = path;
// 从第二个参数开始,转为数组,存入中间件数组 stack 中
info.stack = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1);
} else {
// 如果第一个参数不是路由,则默认是根路由,全部路由都会执行
info.path = '/';
// 从第一个参数开始,转换为数组,存入中间件数组 stack 中
info.stack = slice.call(arguments, 0);
}
return info;
}
use() {
const info = this.register.apply(this, arguments);
this.routes.all.push(info);
}
get() {
const info = this.register.apply(this, arguments);
this.routes.get.push(info);
}
post() {
const info = this.register.apply(this, arguments);
this.routes.post.push(info);
}
match(method, url) {
let stack = [];
// 忽略浏览器自带的 icon 请求
if (url === "/favicon.ico") {
return stack;
}
// 获取 routes
let curRoutes = [];
curRoutes = curRoutes.concat(this.routes.all); // use() 会在所有路由执行
curRoutes = curRoutes.concat(this.routes[method]); // 根据请求方法获取对应路由
curRoutes.forEach(route => {
if (url.indexOf(route.path) === 0) {
// 判断是否属于当前路由或子路由,如果是,则取出
stack = stack.concat(route.stack);
}
})
return stack;
}
// 核心的 next 机制
handle(req, res, stack) {
const next = () => {
// 中间件队列出队,拿到第一个匹配的中间件
// stack 数组是同一个,所以每执行一次 next(),都会取出下一个中间件
const middleware = stack.shift();
if (middleware) {
// 执行中间件函数
middleware(req, res, next);
}
}
// 立马执行
next();
}
callback() {
return (req, res) => {
res.json = (data) => {
res.setHeader('Content-type', 'application/json');
res.end(JSON.stringify(data));
};
const url = req.url;
const method = req.method.toLowerCase();
// 根据方法区分哪些函数需要执行
const resultList = this.match(method, url);
this.handle(req, res, resultList);
}
}
listen(...args) {
const server = http.createServer(this.callback());
server.listen(...args);
}
}
module.exports = () => {
return new LikeExpress();
}
运行 test.js,访问 http://localhost:7878/,结果如下:
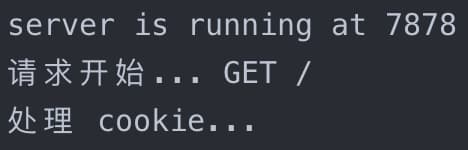
访问 http://localhost:7878/api,结果如下:

六、模拟实现一个 Koa
下面来模拟实现一个 Koa:
- 实现中间件函数的注册;
- 实现中间件函数中核心的洋葱圈 next 机制;
- koa 不涉及路由,所以没有 path 和 method 处理的逻辑。
1、Koa 类的基本结构
先确定这个类要实现的主要方法:
use():实现通用的中间件注册;listen():相当于 httpServer 的listen()函数,可直接在类的listen()函数中创建 httpServer,透传 server 参数,监听请求,并执行回调函数(req, res) => {}。
LikeKoa2 类基本结构如下:
class LikeKoa2 {
constructor() {
// 中间件存储的地方
this.middlewares = [];
}
// 注册中间件
use(fn) {
this.middlewares.push(fn);
return this; // 链式调用
}
callback() {
return (req, res) => {
// ...
}
}
listen(...args) {
const server = http.createServer(this.callback());
server.listen(...args);
}
}
2、洋葱圈 next 机制实现
koa 的中间件函数是参数为 ctx、next 的 async 函数,首先实现 koa 最核心的洋葱圈 next 机制。next 的参数是个 async 函数,调用它才可以一层一层的调用下一个中间件函数,因此 next 函数需要:
- 返回
Promise函数; - 从中间件数组中取出第一个中间件,然后迭代地取出下一个中间件,直到里层的中间件一层一层从里向外执行完,从而实现洋葱圈执行的效果。
// 闭包保存中间件
function compose(middlewareList) {
return function (ctx) {
// 洋葱圈 next 机制核心方法
function dispatch(i) {
// 取出第 i 个位置的洋葱圈
const fn = middlewareList[i];
try {
// Promise.resolve 包裹以防 fn 不是 Promise
return Promise.resolve(
// 返回下一层洋葱圈,实现 next 机制
fn(ctx, dispatch.bind(null, i + 1))
);
} catch (e) {
return Promise.reject(e);
}
}
// 从第一个中间件开始从里向外执行
return dispatch(0);
}
}
中间件函数的 next 不是直接调用的下一个中间件函数,而是调用的 fn 内部的 dispatch 函数,由它来调用下一个中间件函数并传递上下文对象(ctx)和自身(dispatch)。
一个中间件函数执行完毕,相应的 dispatch 函数将执行权转交给上一个中间件函数的 await next() 执行该中间件函数 await 后续的代码。
3、创建上下文 context
Koa 每个请求都将创建一个 Context,并在中间件中作为接收器引用,或者 ctx 标识符。
createContext(req, res) {
const ctx = {
req,
res,
};
// ...more
// koa 的创建上下文的函数会更丰富一点,这里为了简化实现只封装了 req 和 res
return ctx;
}
4、将上下文对象传入中间件函数中
上面通过 compose 组合中间件函数返回了一个接收 ctx 上下文参数的函数,所以只需再建立一个 handleRequest 函数,把创建好的上下文对象传入此函数即可:
// 把上下文传入中间件函数
handleRequest(ctx, fn) {
return fn(ctx);
}
在 callback 函数中使用:
callback() {
// 组合中间件
const fn = compose(this.middlewares);
return (req, res) => {
// 创建上下文对象
const ctx = this.createContext(req, res);
// 将上下文传入中间件
return this.handleRequest(ctx, fn);
}
}
5、测试实现的 Koa
下面验证 LikeKoa2 类是否实现了中间件注册收集和洋葱圈 next 机制:
- test.js
- like-koa2.js
const Koa = require('./like-koa2')
const app = new Koa()
// 注册第一个中间件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
console.log('1、第一层洋葱 --> 开始')
await next()
console.log('2、第一层洋葱 --> 结束')
})
// 注册第二个中间件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
console.log('3、第二层洋葱 --> 开始')
await next()
console.log('4、第二层洋葱 --> 结束')
})
// 注册第三个中间件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
console.log('5、第三层洋葱 --> 开始')
console.log('6、第三层洋葱 --> 结束')
})
app.listen(3333, () => {
console.log('server is running on port 3333')
})
const http = require('http');
// 闭包保存中间件
function compose(middlewareList) {
return function (ctx) {
// 洋葱圈 next 机制核心方法
function dispatch(i) {
// 取出第 i 个位置的洋葱圈
const fn = middlewareList[i];
try {
// Promise.resolve 包裹以防 fn 不是 Promise
return Promise.resolve(
// 返回下一层洋葱圈,实现 next 机制
fn(ctx, dispatch.bind(null, i + 1))
);
} catch (e) {
return Promise.reject(e);
}
}
// 从第一个中间件开始从里向外执行
return dispatch(0);
}
}
class LikeKoa2 {
constructor() {
// 中间件存储的地方
this.middlewares = [];
}
// 注册中间件
use(fn) {
this.middlewares.push(fn);
return this; // 链式调用
}
createContext(req, res) {
const ctx = {
req,
res,
};
return ctx;
}
// 把上下文传入中间件函数
handleRequest(ctx, fn) {
return fn(ctx);
}
callback() {
// 组合中间件
const fn = compose(this.middlewares);
return (req, res) => {
// 创建上下文对象
const ctx = this.createContext(req, res);
// 将上下文传入中间件
return this.handleRequest(ctx, fn);
}
}
listen(...args) {
const server = http.createServer(this.callback());
server.listen(...args);
}
}
module.exports = LikeKoa2;
运行 test.js,访问 http://localhost:3333/,结果如下:

具体流程如下:
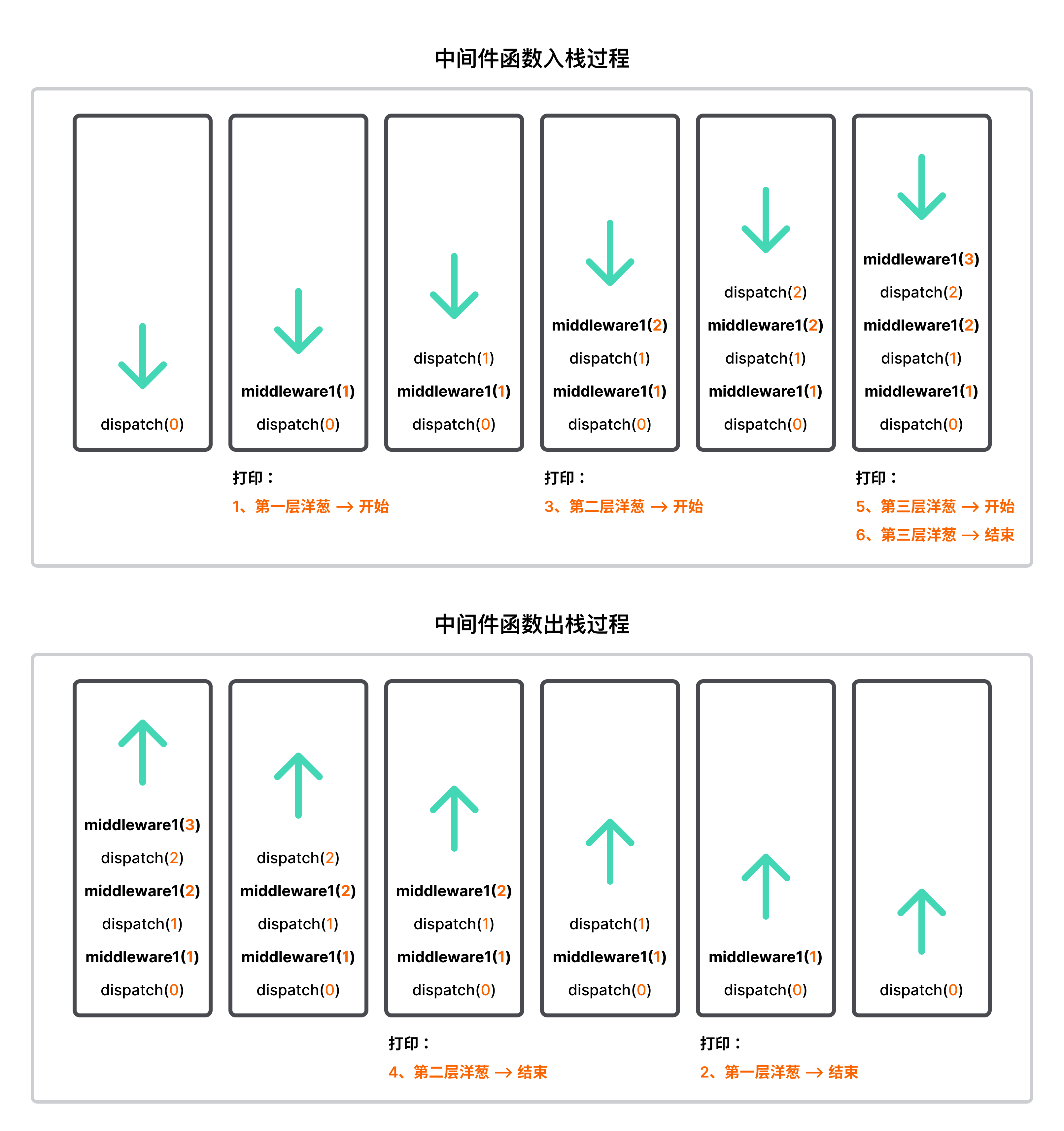
fn 根据自定义下标 i 取出 middleware 栈中的第一个中间件函数并执行,将上下文对象 ctx 和 dispatch.bind(null, i+1) 作为参数传递给中间件函数。
- 首先执行
console.log('1、第一层洋葱 --> 开始')打印; - 然后执行
await next()将当前中间件函数的执行权转交给 next(即:dispatch(1))执行; - 继续取出第二个中间件函数执行,以此类推,直到所有中间件都执行完毕;
- 最后执行的中间件函数出栈后,将执行权转交给前一个中间件函数的
await出,继续代码的执行。