React 高阶组件(HOC)
一、高阶组件的定义
高阶组件(Higher-order function)是 React 中用于复用组件逻辑的技巧,基于装饰器设计模式,它不是组件,而是一个纯函数,接受一个组件作为参数并返回改造后的新组件。
// 接受一个组件 WrappedComponent 作为参数,返回加工后的新组件 EnhancedComponent
const EnhancedComponent = highOrderComponent(WrappedComponent)
组件与高阶组件的区别:组件是将 props 转为 UI,而高阶组件是将组件转为另一个组件。
Hook 会替代高阶组件吗?
高阶组件可以外部协议化注入功能到一个组件中,可以用来做插件,通过注入状态化的 props 的方式对组件进行功能扩展,而不是直接将代码写在主库中。而 Hook 的处理会与组件强依赖,不是用来解决插件注入问题的。
二、高阶组件的作用
1、复用逻辑
高阶组件可以看作一个加工 React 组件的工厂,批量对原有组件进行加工处理。可以根据业务需求定制专属的高阶组件,实现逻辑的复用。
2、强化 props
高阶组件返回的组件,可以劫持上一层传过来的 props,然后混入新的 props 来增强组件的功能。例如 react-router 中的 withRouter。
3、组件赋能
高阶组件可以给组件提供一些拓展功能,例如额外的生命周期和额外的事件。典型案例 react-keepalive-router 中的 keepaliveLifeCycle 就是通过高阶组件,给业务组件增加了额外的生命周期。
4、渲染劫持
渲染劫持是高阶组件的一个特性,可以对原来的组件进行条件渲染,控制组件的渲染逻辑,常用于权限控制,或 react-redux 中的 connect。
在实际应用中,高阶组件常用于与核心业务无关但又在多个模块使用的功能,如权限控制、日志记录、数据校验、异常处理、统计上报等功能。
三、高阶组件的编写与使用
1、如何编写
下面编写一个 HOC,对传入的 WrappedComponent 组件执行以下操作:
- 添加 color 属性值为 #9189F7
- 保留原组件的
props,同时对props中的 count 进行两倍赋值的处理
// 函数包裹的写法
const EnhancedComponent = (WrappedComponent) => {
return function Temp(props) { // 注意这里需要返回具名函数,不能使用箭头函数(this 绑定问题)
const [txtColor, setTxtColor] = useState('#9189F7')
return (
<WrappedComponent
color={txtColor}
{...props}
count={props.count * 2}
/>
)
}
}
// 类包裹的写法
const EnhancedComponent = (WrappedComponent) => {
return class extends React.Component { // 这里 class 可以不带名字
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
txtColor: '#9189F7'
}
}
render() {
return (
<WrappedComponent
color={this.state.txtColor}
{...this.props}
count={this.props.count * 2}
/>
)
}
}
}
通过对传入的原始组件 WrappedComponent 执行想要的操作(操作 props、提取 state、给原始组件包裹其他元素等),从而加工出想要的组件 EnhancedComponent。
2、在函数组件使用
import React, { useState } from "react";
// 编写 HOC
const EnhancedComponent = (WrappedComponent) => {
return function Temp(props) {
const [txtColor, setTxtColor] = useState("#9189F7");
return (
<WrappedComponent
color={txtColor}
count={props.count * 2}
{...props}
/>
);
};
};
// 函数组件
const TestComponent = ({ color, count, unit }) => {
return (
<div style={{ color: color }}>
{count}
{unit}
</div>
);
};
// 使用 HOC 装饰函数组件
const EnhancedTestComponent = EnhancedComponent(TestComponent);
// 使用 EnhancedTestComponent 组件
const UseComponent = () => {
return <EnhancedTestComponent count={23} unit="岁" />;
};
export default UseComponent;
页面显示颜色为 #9189F7 的 "46岁" 文本。
3、在类组件使用
import React, { useState } from 'react'
// 编写 HOC
const EnhancedComponent = (WrappedComponent) => {
return function Temp(props) {
const [txtColor, setTxtColor] = useState('#9189F7')
return (
<WrappedComponent
color={txtColor}
count={props.count * 2}
{...props}
/>
)
}
}
// 使用 HOC 装饰组件 TestComponent
@EnhancedComponent
class TestComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div style={{ color: this.props.color }}>
{this.props.count}
{this.props.unit}
</div>
)
}
}
// 使用 TestComponent 组件
const UseComponent = () => {
return <TestComponent count={23} unit="岁" />
}
export default UseComponent
正常情况下,页面会显示颜色为 #9189F7 的 "46岁" 文本。但如果没配置好可能会出现报错,需要解决下面几个问题:
2-1、安装 Babel 插件兼容装饰器 @
安装 @babel/plugin-proposal-decorators 以兼容 ES7 装饰器 @ 的写法:
npm install --save-dev @babel/plugin-proposal-decorators
# 或
yarn add @babel/plugin-proposal-decorators -D
配置 Babel:
"babel": {
"presets": [
// ...
],
"plugins": ["@babel/plugin-proposal-decorators"]
},
配置完这一步,会出现以下报错:
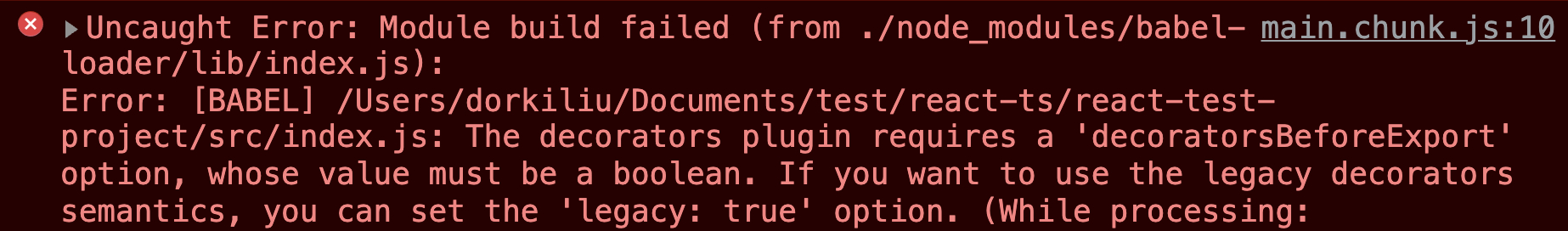
需要设置 legacy 属性为 true:
"babel": {
"presets": [
// ...
],
"plugins": [
[
"@babel/plugin-proposal-decorators",
{
"legacy": true
}
]
]
},
2-2、解决编辑器报错
配置完装饰器 @ 的 Babel 插件后,编辑器中还会出现以下错误:
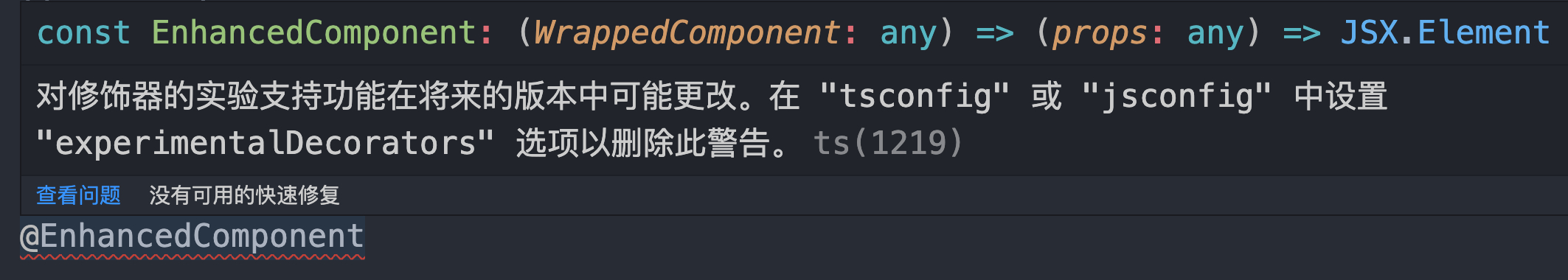
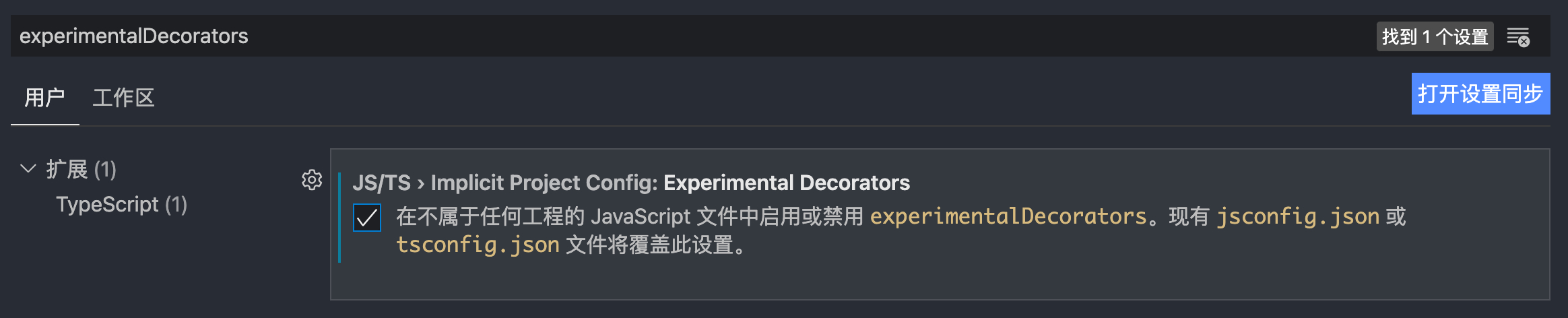
VSCode 直接在设置中搜索 experimentalDecorators 并开启该选项即可:
2-3、保证被装饰者是类或类的方法
如果上面的 TestComponent 是个函数,而不是类或类的方法,会出现以下报错:
Leading decorators must be attached to a class declaration
2-4、HOC 不能添加 ref
高阶组件可以传递 props,但不能传递 ref。因为 ref 实际上不是一个 prop,它是由 React 专门处理的。如果将 ref 添加到 HOC 返回的组件中,则 ref 引用指向容器组件,而不是被包装的组件。
可以使用 ref 转发来解决该问题。
四、高阶组件的应用
高阶组件能够提高代码的复用性和灵活性,在实际应用中,常用于与核心业务无关但又在多个模块使用的功能,如权限控制、日志记录、数据校验、异常处理、统计上报等。
1、组件渲染性能监控
import React from 'react'
const WithTiming = (WrappedComponent) => {
return class extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.start = 0
this.end = 0
this.state = {
loadTime: 0
}
}
componentWillMount() {
this.start = Date.now()
}
componentDidMount() {
this.end = Date.now()
this.setState({
loadTime: this.end - this.start
})
}
render() {
return <WrappedComponent time={this.state.loadTime} />
}
}
}
// 使用 WithTiming 装饰组件 TestComponent
@WithTiming
class TestComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return <div>TestComponent 组件渲染时间为 {this.props.time} ms</div>
}
}
// 使用 TestComponent 组件
const UseComponent = () => {
return <TestComponent />
}
export default UseComponent
输出结果:

2、反向继承与渲染劫持
反向继承就是函数接受一个 WrappedComponent 组件作为参数,并返回一个继承了该 WrappedComponent 组件的类,且在该类的 render() 方法中返回 super.render() 方法。例如:
const EnhancedComponent = (WrappedComponent) => {
// 与上面属性代理的区别在于 extends WrappedComponent 而非 React.Component
return class extends WrappedComponent {
render() {
// 返回 super.render() 方法
return super.render()
}
}
}
反向继承可以用于渲染劫持,渲染劫持就是控制基类组件的 render 函数,可用于篡改 props 或 children。例如劫持 render 替换子节点:
import React from 'react'
const EnhancedComponent = (WrappedComponent) => {
return class extends WrappedComponent {
render() {
const element = super.render()
/* 将第 3 个元素节点 Angular 替换为 @angular/core */
const appendElement = React.createElement('li', {}, '@angular/core')
const newChild = React.Children.map(
element.props.children,
(child, index) => {
if (index === 2) return appendElement
return child
}
)
return React.cloneElement(element, element.props, newChild)
}
}
}
// 使用 EnhancedComponent 装饰组件 TestComponent
@EnhancedComponent
class TestComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<ul>
<li>React</li>
<li>Vue</li>
<li>Angular</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
// 使用 TestComponent 组件
const UseComponent = () => {
return <TestComponent />
}
export default UseComponent
输出结果:

点击查看更多案例实践(强化 prop - withRoute、控制渲染 connect、缓存生命周期 keepaliveLifeCycle 等)
五、总结
什么是高阶组件?
高阶组件是 React 中用于复用组件逻辑的技巧,基于装饰器设计模式,它不是组件,而是一个纯函数,接受一个组件作为参数并返回改造后的新组件。主要用于代码逻辑复用、强化 props、组件赋能和渲染劫持,以提高开发效率和代码的可维护性。
组件与高阶组件的区别?
组件是将 props 转为 UI,而高阶组件是将组件转为另一个组件。
Hook 会替代高阶组件吗?
高阶组件可以用来做插件,通过注入状态化的 props 的方式对组件进行功能扩展,而不是直接将代码写在主库中。而 Hook 的处理会与组件强依赖,不是用来解决插件注入问题的。